Using AI to improve radiologist performance in detecting abnormalities on chest radiographs
Population
500 chest X-rays with CT scanner performed within 72 hours from Hôpital Cochin (AP-HP)
Design
Gold standard: CT-based annotation by chest radiologist
Readers: 4 chest radiologists, 4 general radiologists, 4 radiology residents
MRMC study design: reading with and without AI
Highlights
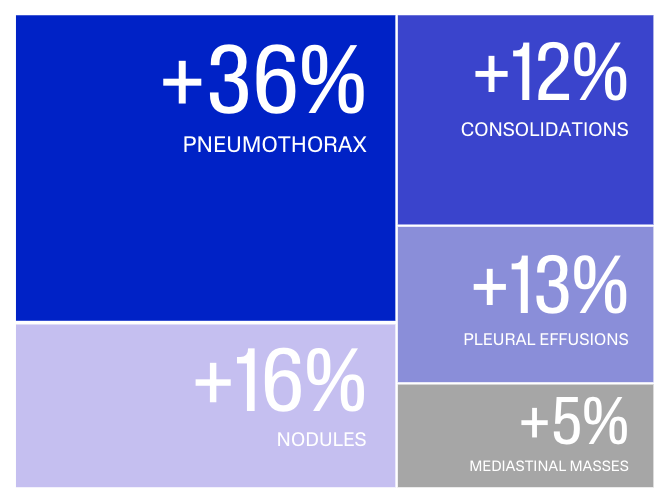
AI-assisted chest radiography interpretation resulted in an increased sensitivity of 5.9 to 26.2 % (P<.001) for all readers including thoracic radiologists, general radiologists, and radiology residents.
General radiologists and radiology residents assisted by AI achieved the performance of chest radiologists without AI
Mean reading time was 81s without AI vs 56s with AI (-31%, P<.001), with a 17% reduction for radiographs with abnormalities vs 38% for no abnormalities.
Conclusion
AI assistance can improve the detection accuracy of thoracic abnormalities on chest radiographs across radiologists of varying expertise, leading to marked improvements in sensitivity and a reduction in interpretation time.