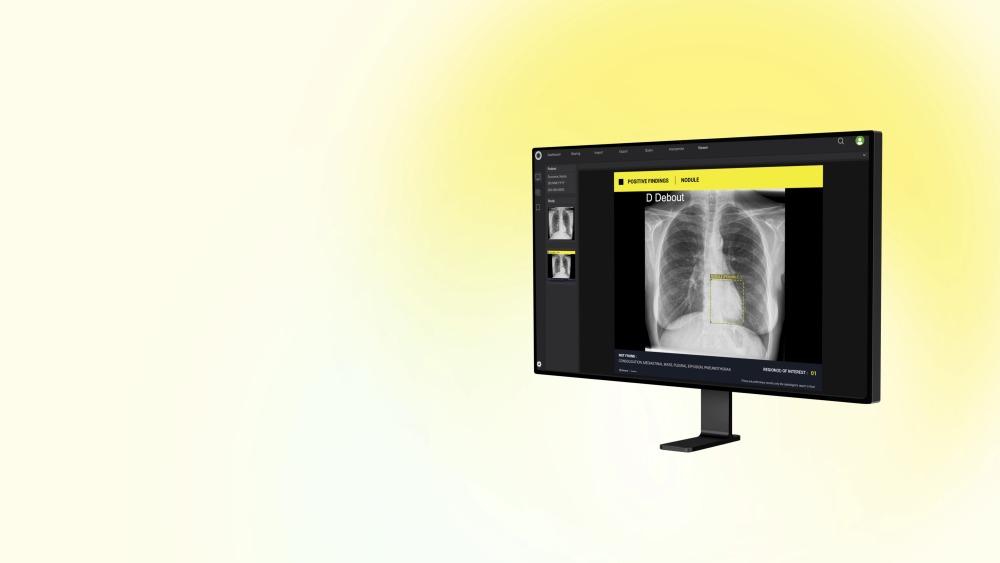
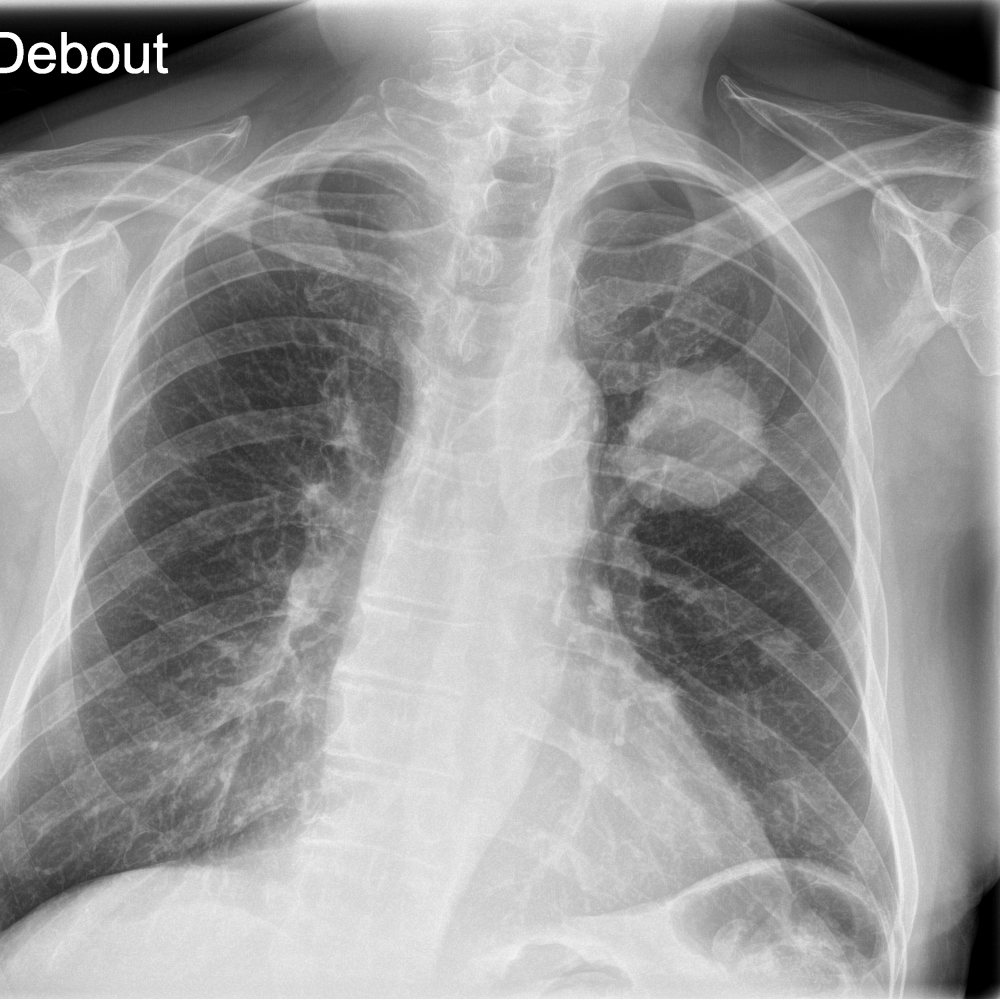
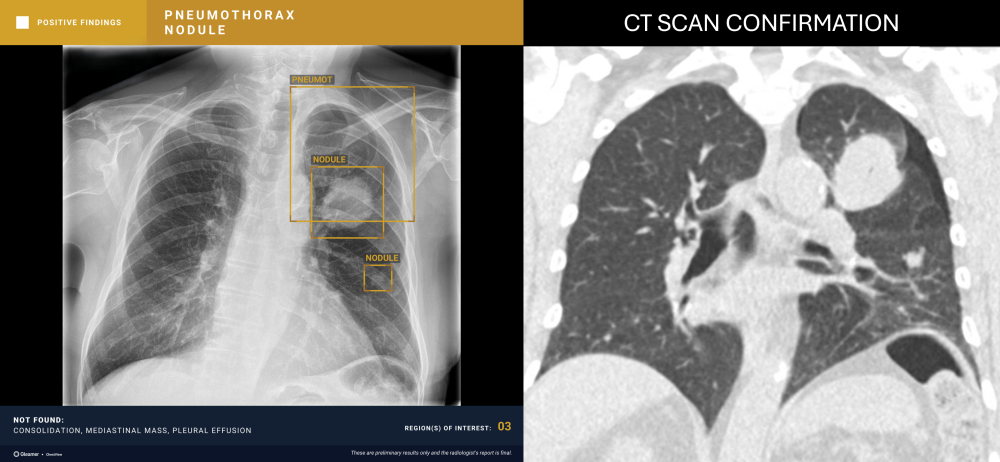
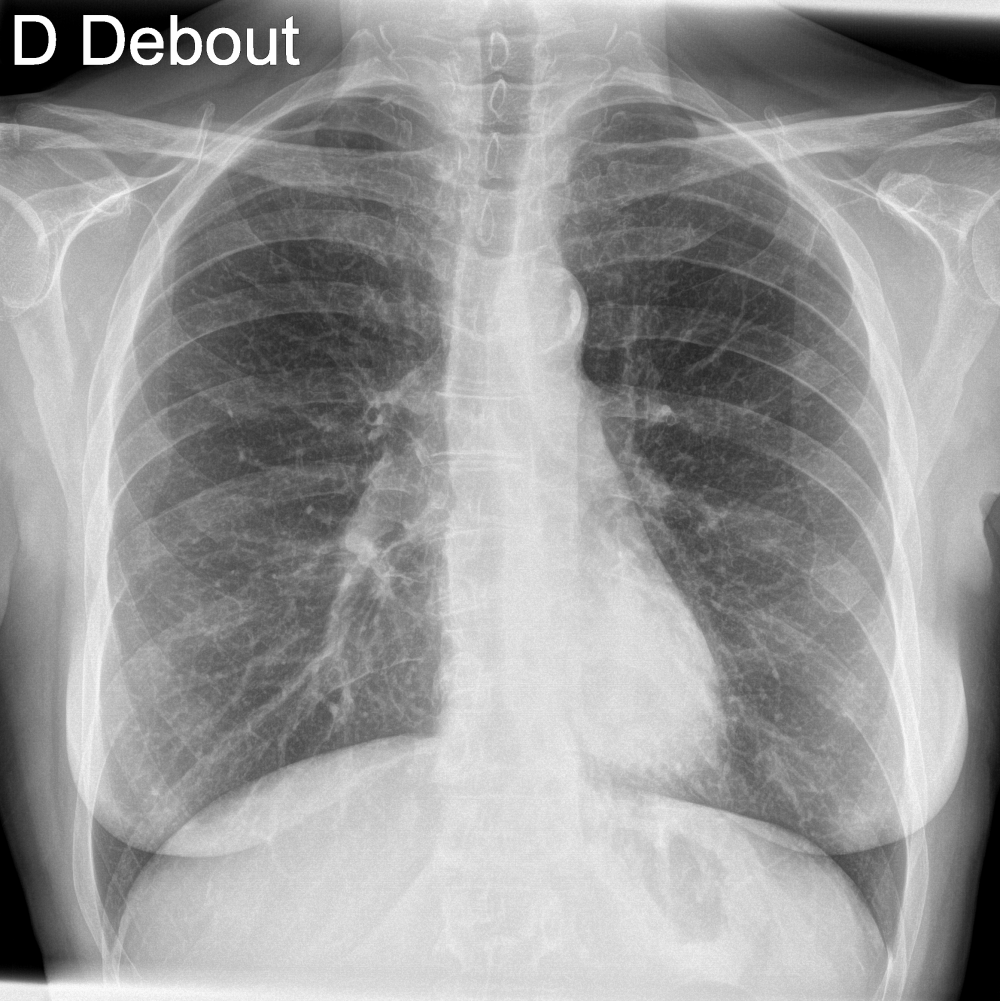
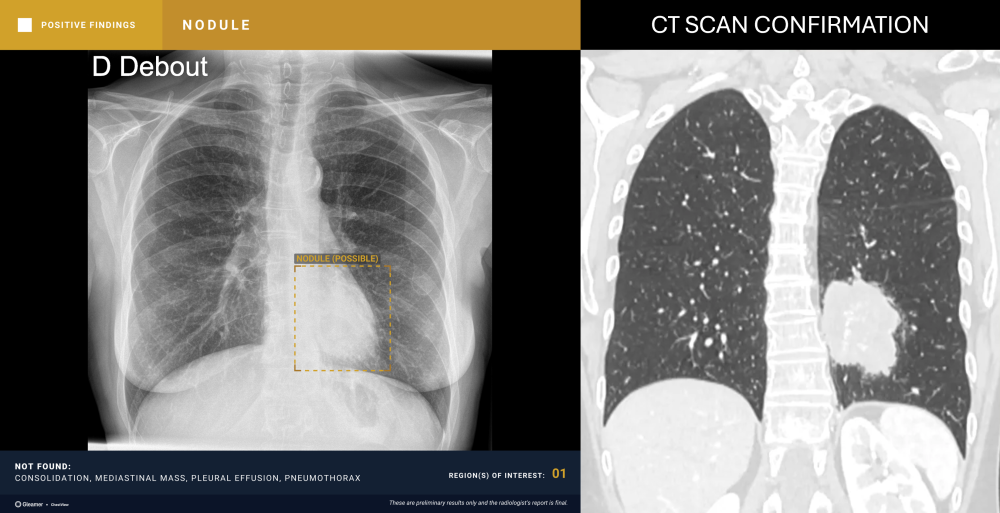
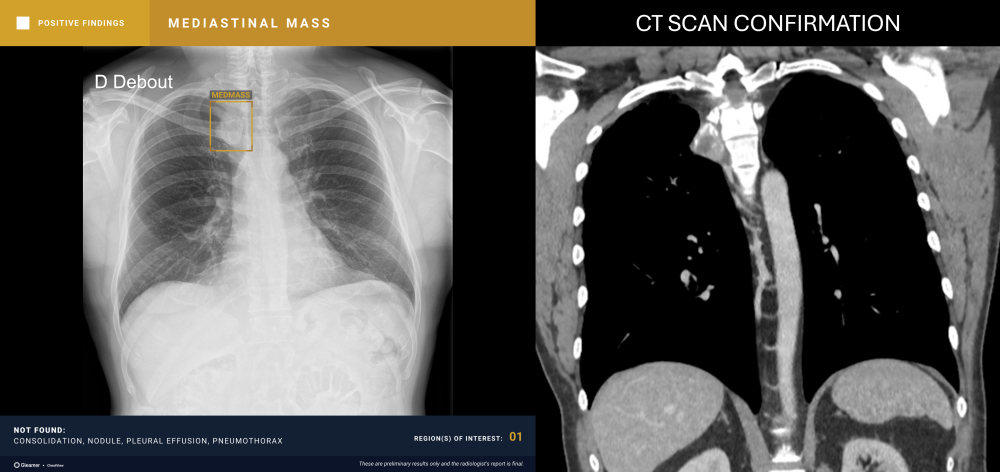
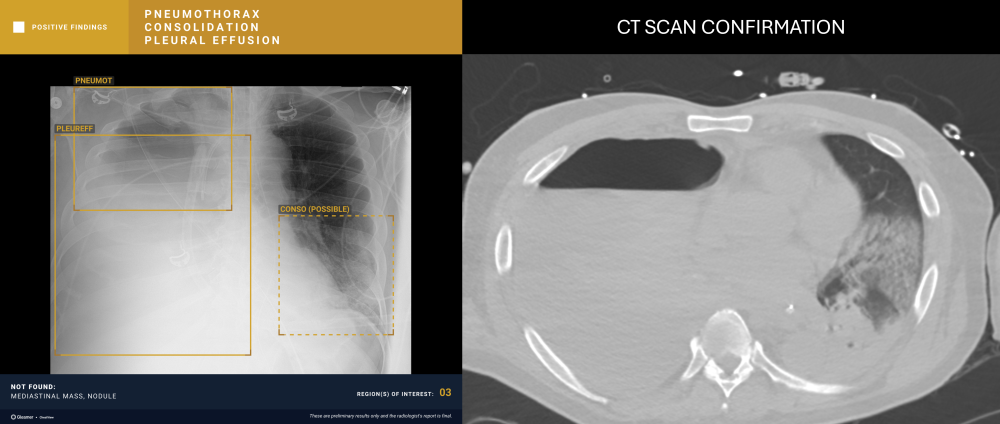
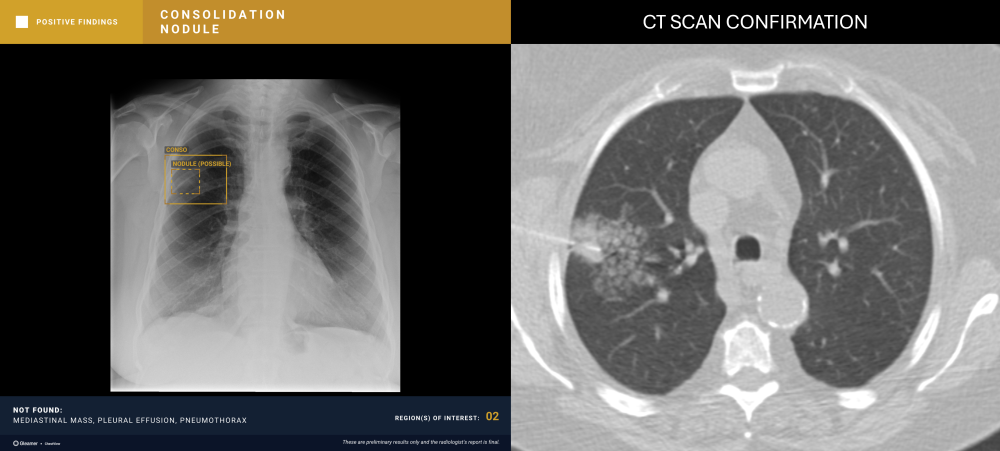
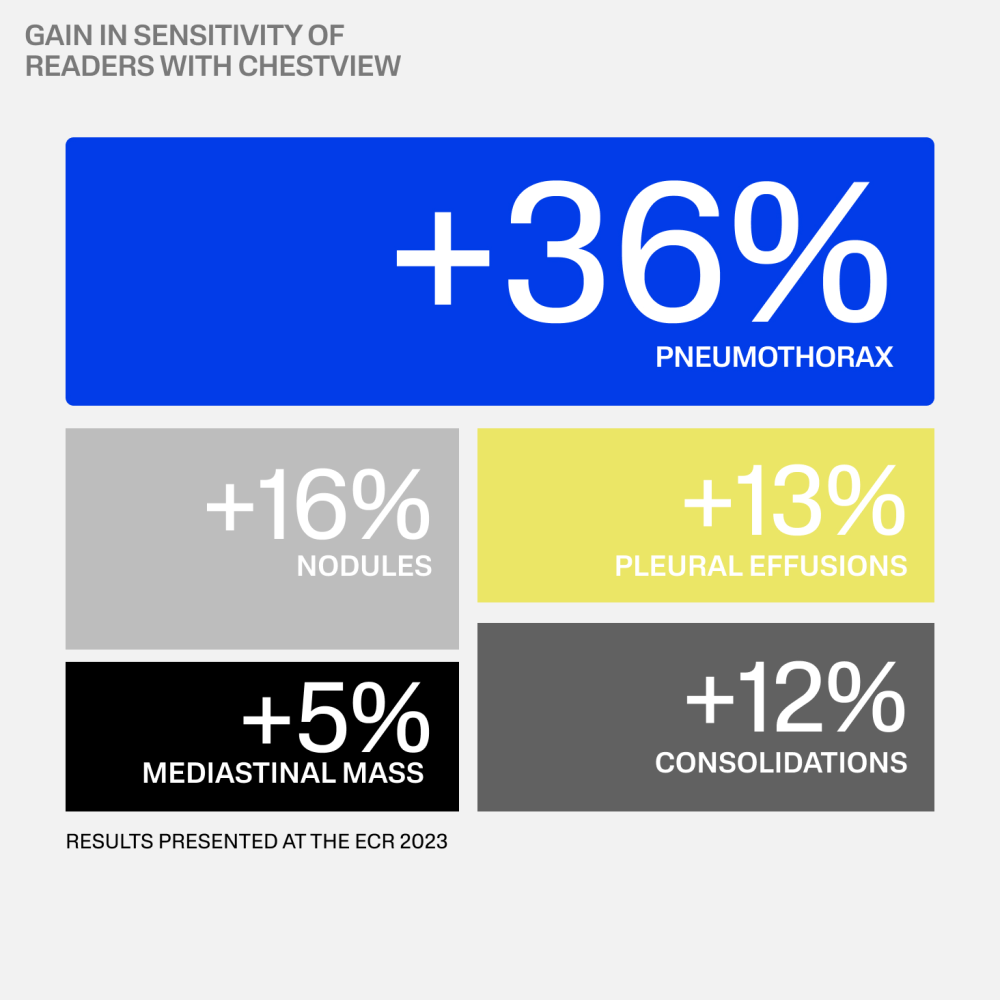
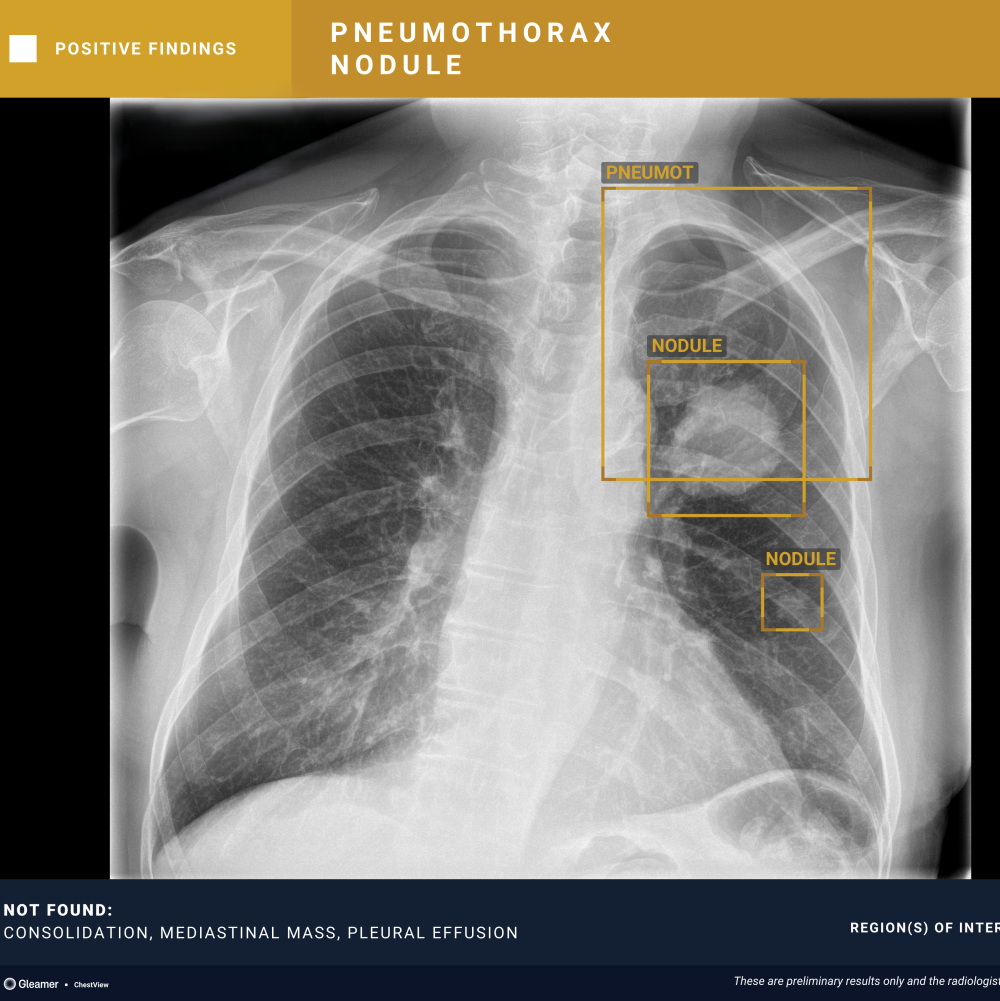
“CXR is the 1st line exam for multiple indications, however, CXR reading is particularly difficult. AI has the ability to detect subtle findings that require urgent management or that can highly impact patient prognosis, including signs of cancer, increasing the performance of radiologists.”